NEWS&EVENTS
Home > News&Events > Company news > High-efficiency extraction process of antimony ingot and antimony trioxide
In the field of antimony metal smelting, there are many mature and efficient process methods. The following will introduce two common antimony smelting processes in detail:
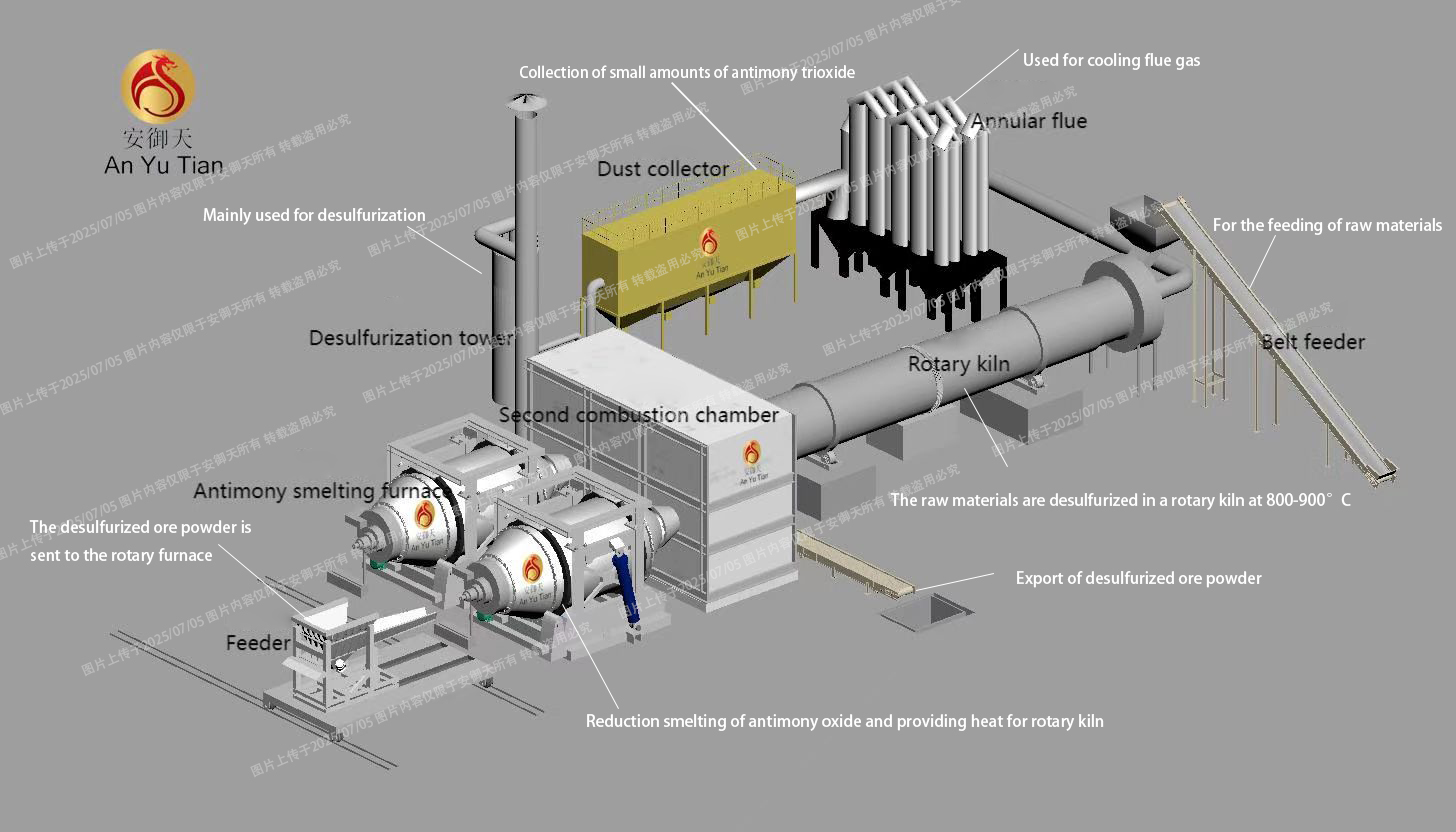
1. Pyrometallurgy
Purpose: Focus on the precise extraction of high-purity antimony ingots and antimony trioxide from antimony ore.
Core equipment: Mainly rely on rotary kilns and rotary smelting furnaces to complete key processes.
Process flow: Antimony ore is first sent to a rotary kiln for roasting and desulfurization. The ore powder obtained after this step is smoothly transported to the rotary furnace through a feeder, and reduced smelting is carried out under high temperature to finally produce crude antimony metal. The high-temperature flue gas generated during the smelting process is first cooled through an annular flue, and then enters a bag filter, where a small amount of antimony trioxide powder can be collected. Finally, the flue gas is deeply purified through a desulfurization tower. If refined antimony or antimony trioxide is to be further obtained, the crude antimony and the refining agent must be fully refined in a refining furnace. After obtaining antimony liquid, antimony ingots or antimony oxide powder are finally obtained by using a continuous casting machine or an oxidation furnace and a dust removal system.
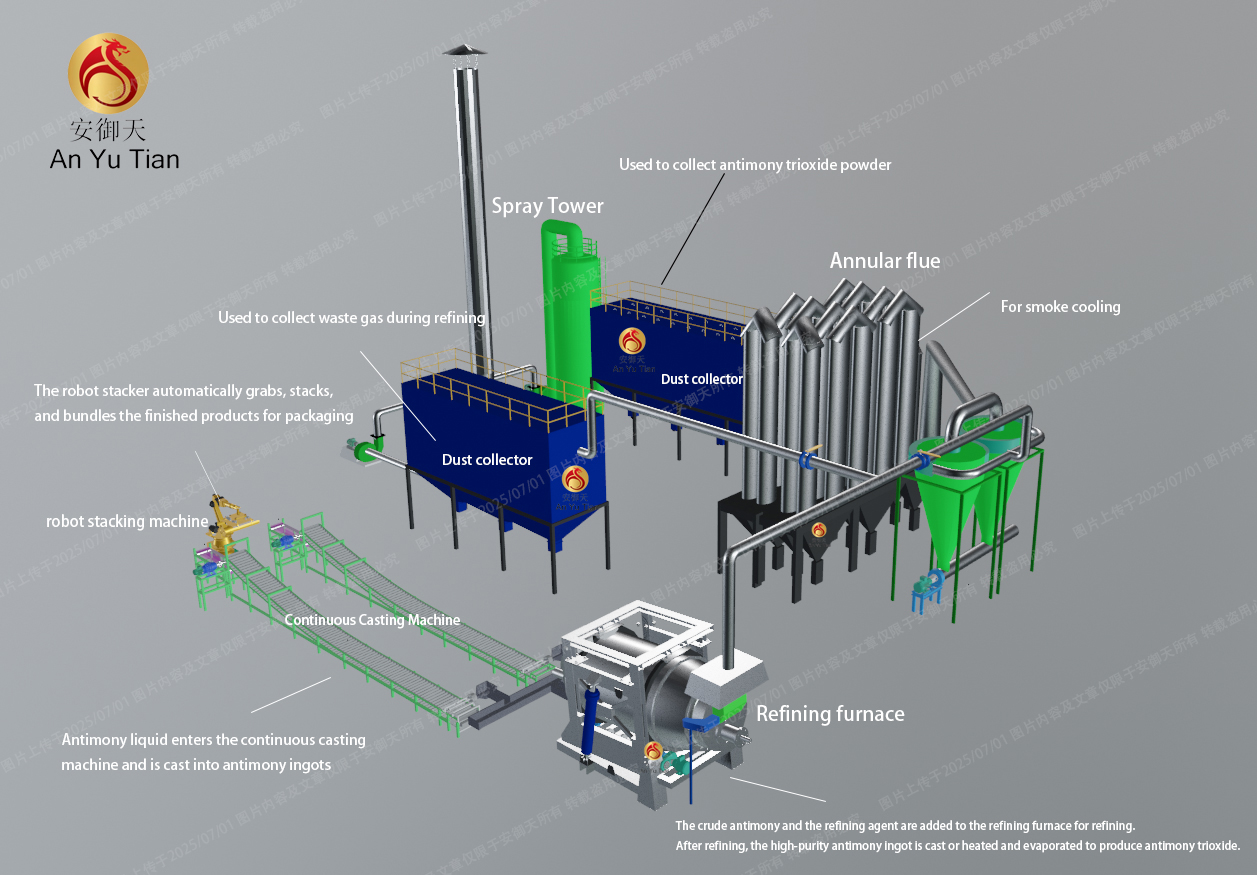
2. Fire method - electrolysis combined with smelting
Core equipment: mainly composed of electrolysis equipment such as rotary furnace and electrolytic cell.
Process flow: Antimony ore is first subjected to high-temperature desulfurization in a rotary furnace to obtain antimony oxide powder. Then, the antimony ore powder is subjected to high-temperature reduction smelting in a rotary furnace to produce crude antimony, which is made into antimony anode plates through a smelting and casting process, and then enters the electrolytic refining stage. During the electrolysis process, high-purity antimony is precipitated at the cathode and then made into high-purity antimony ingots through a smelting and casting process. In order to produce Sb2O3 powder, the high-purity antimony ingot needs to be remelted and volatilized and oxidized in a high-temperature strong oxidizing atmosphere. The gaseous Sb2O3 is quickly condensed and finally forms a powdered product.
These two antimony smelting processes have their own characteristics and advantages. In actual production, they can be reasonably selected according to factors such as ore properties and product requirements to achieve efficient and high-quality antimony metal production.