NEWS&EVENTS
The primary purpose of roasting antimony ore in a rotary kiln, besides effective desulfurization, is also crucial in many other respects. From the perspective of optimizing ore composition, antimony ore often contains a variety of impurity minerals, such as carbonates and sulfides. At high temperatures of 800-900°C, these impurities undergo a series of complex physical and chemical changes. Carbonate impurities decompose, releasing carbon dioxide gas, thereby reducing the carbonate content in the ore and minimizing potential gas interference during subsequent smelting, making the smelting process more stable and controllable. Sulfide impurities react with oxygen at high temperatures, not only desulfurizing the ore but also converting some sulfides into more stable oxides, improving the ore's chemical properties and creating more favorable conditions for subsequent high-temperature reduction smelting in the rotary kiln.
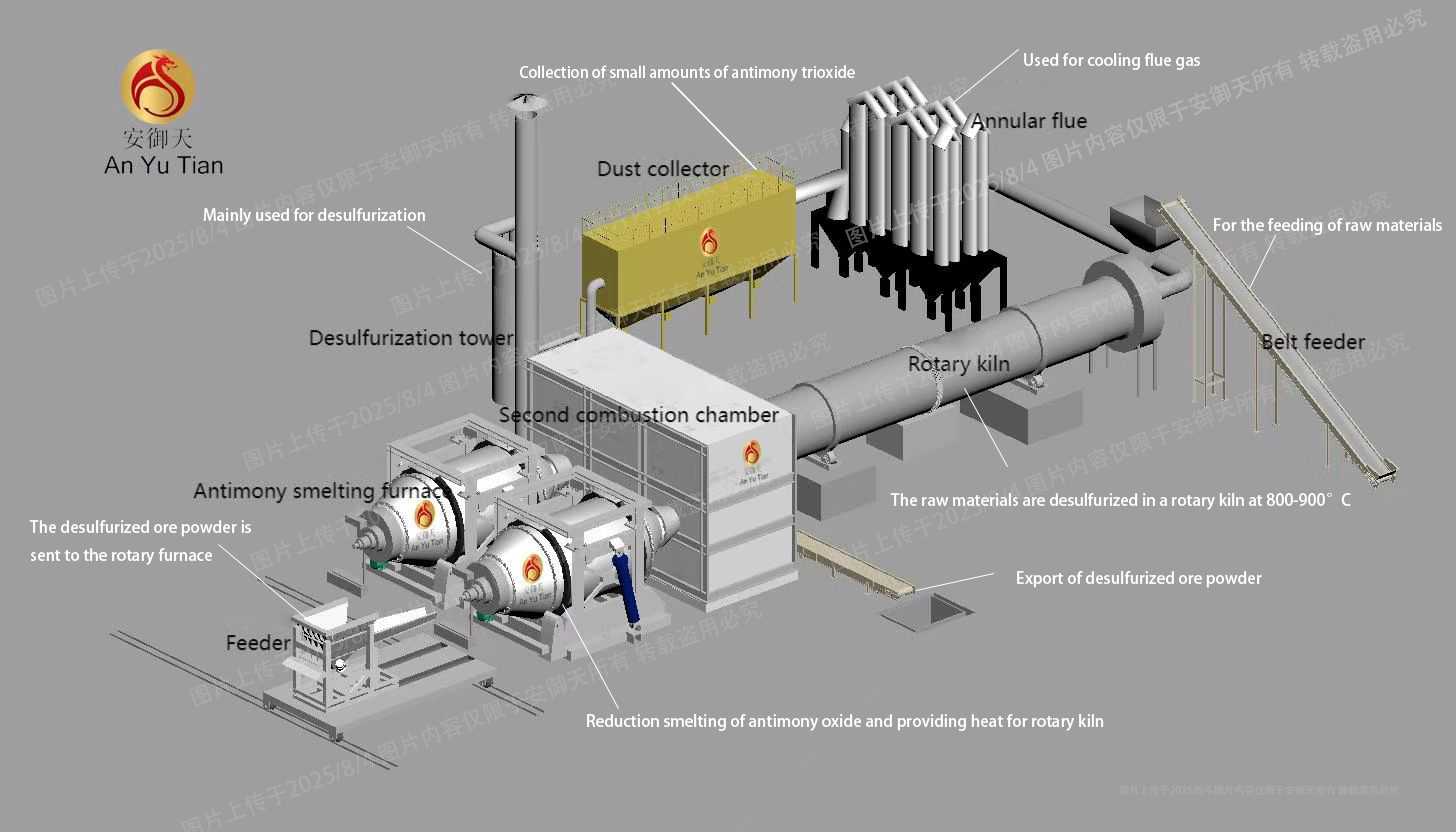
From the perspective of improving metal recovery, the roasting process can alter the occurrence state of antimony in antimony ore. Antimony may originally exist in the ore as complex compounds. After high-temperature roasting, some of these compounds decompose or undergo phase transformation, making the antimony more readily available for recovery during subsequent smelting. This process acts as a pretreatment of the ore, breaking the tight bond between antimony and impurities, increasing the activity and extractability of antimony in subsequent smelting steps, and significantly improving antimony metal recovery while reducing resource waste.
Roasting also plays a role in consolidation and agglomeration. Under high temperatures, the ore particles partially melt and bond, transforming the loose ore powder into a blocky material with a certain strength and porosity. This blocky material, when entering the rotary kiln for high-temperature reduction smelting, is better able to contact the reducing agent, ensuring a uniform reduction reaction. It also facilitates gas circulation within the rotary kiln, improving heat and mass transfer efficiency, and further enhancing the efficiency and quality of the entire smelting process.