NEWS&EVENTS
Home > News&Events > Company news > The whole process of producing antimony trioxide by pyrometallurgical and electrolytic refining of antimony ore
Antimony is widely used in many fields such as electronics, chemical industry, and metallurgy. From antimony ore to high-purity antimony products and antimony compounds, a series of complex and delicate processing procedures are required. The following will introduce the main process flow of antimony ore pyrometallurgy and electrolytic refining in detail.
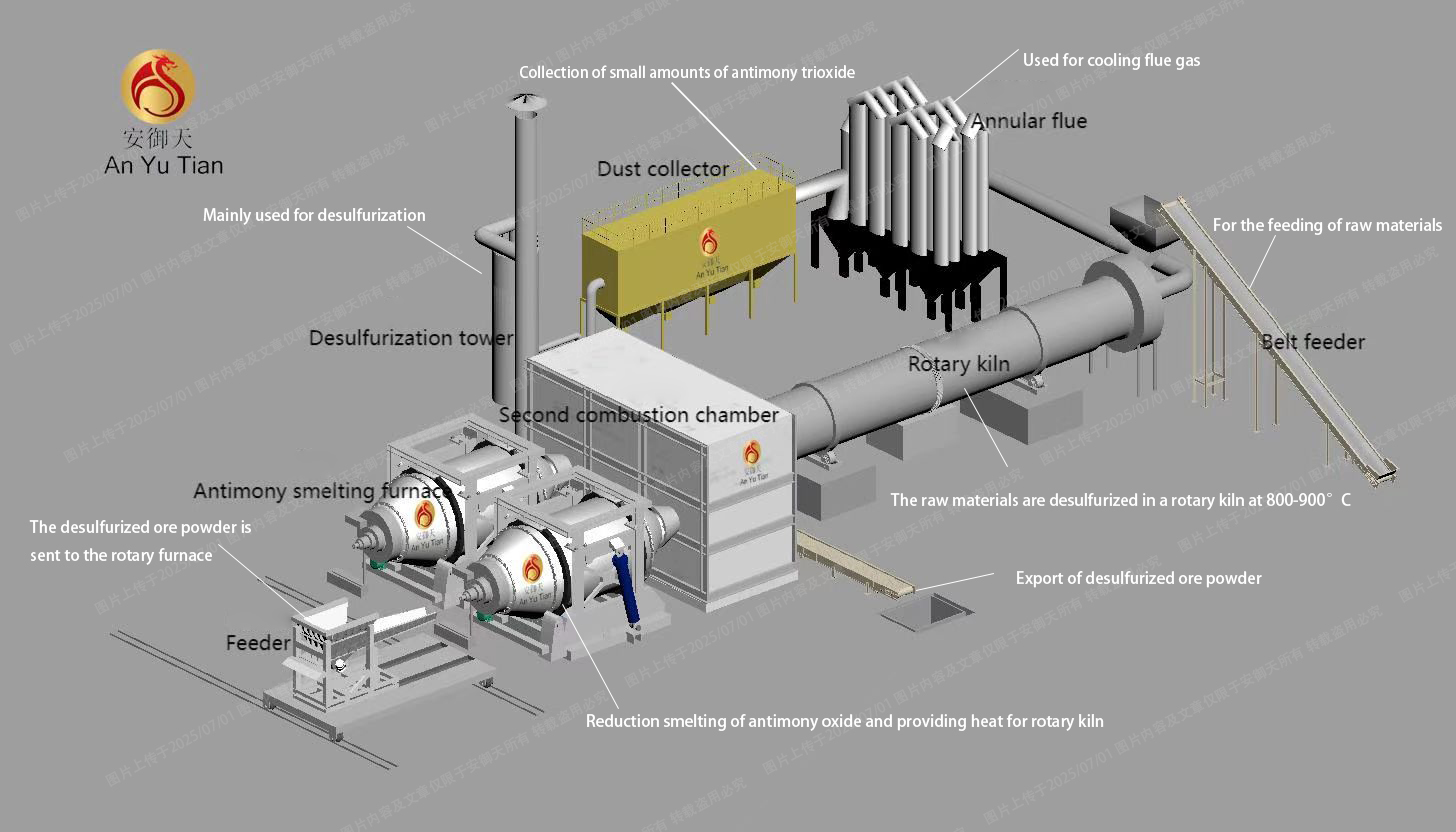
1. High-temperature desulfurization in a rotary furnace
The antimony ore is placed in a rotary furnace, and the roasting temperature is strictly controlled at 800-1000℃, while introducing an appropriate amount of air. Under high temperature and limited air, the sulfur element in the ore is oxidized to SO2 gas and escapes, and the antimony ore is transformed into antimony oxide powder rich in antimony oxide, realizing the effective separation of antimony and sulfur, laying the foundation for subsequent processes.
2. High-temperature reduction smelting
The desulfurized antimony ore powder is sent to a rotary furnace, and a reducing agent is added to raise the temperature in the furnace to about 1200℃. At this high temperature, antimony oxide reacts with the reducing agent and is reduced to metallic antimony, producing crude antimony. Because crude antimony contains impurities, it needs to be melted and cast into antimony anode plates to enter the electrolytic refining stage.
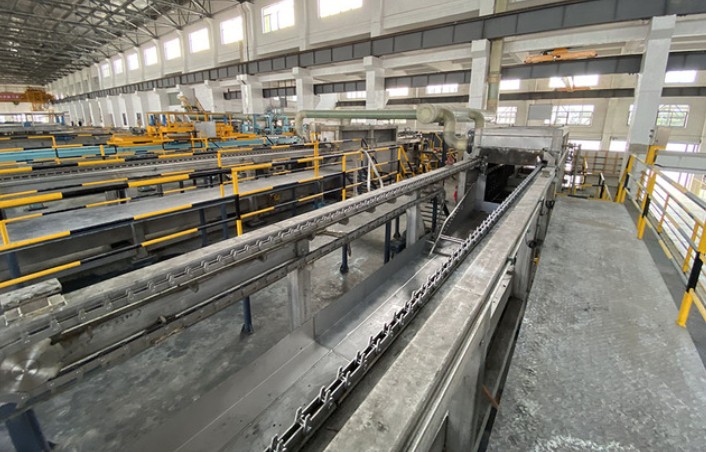

3. Electrolytic refining
Antimony anode plates are used as anodes, placed in a specific electrolyte system and connected to a power supply. Under the action of the current, the antimony at the anode dissolves into the electrolyte, and precious metals such as silver and gold remain in the anode mud due to their stable chemical properties, which can be recycled later. In the cathode area, high-purity antimony precipitates from the electrolyte to form cathode antimony, which is then made into high-purity antimony ingots through a smelting and casting process.
4. Sb2O3 powder production
High-purity antimony ingots need to undergo remelting and high-temperature evaporation oxidation. The high-purity antimony ingot is placed in an oxidation furnace, and the melting temperature is controlled at about 1000°C. After melting, a high-temperature strong oxidizing atmosphere is created to volatilize and oxidize the molten antimony to generate gaseous Sb2O3. Gaseous Sb2O3 enters the quenching zone (such as a bag dust collector) and condenses rapidly to form fine cubic Sb₂O₃ powder. In production, key parameters such as temperature, atmosphere and condensation rate must be precisely controlled to obtain flame-retardant grade Sb2O3 products with uniform particle size, high whiteness and excellent reaction activity.
Through the above series of process flows such as high-temperature desulfurization in rotary furnace, high-temperature reduction smelting, electrolytic refining and Sb2O3 powder production, the transformation from antimony ore to high-purity antimony ingot and flame-retardant grade Sb2O3 products is realized. These processes not only make full use of antimony ore resources, but also improve the quality and added value of antimony products through fine processing, meeting the needs of different fields for antimony and its compounds.